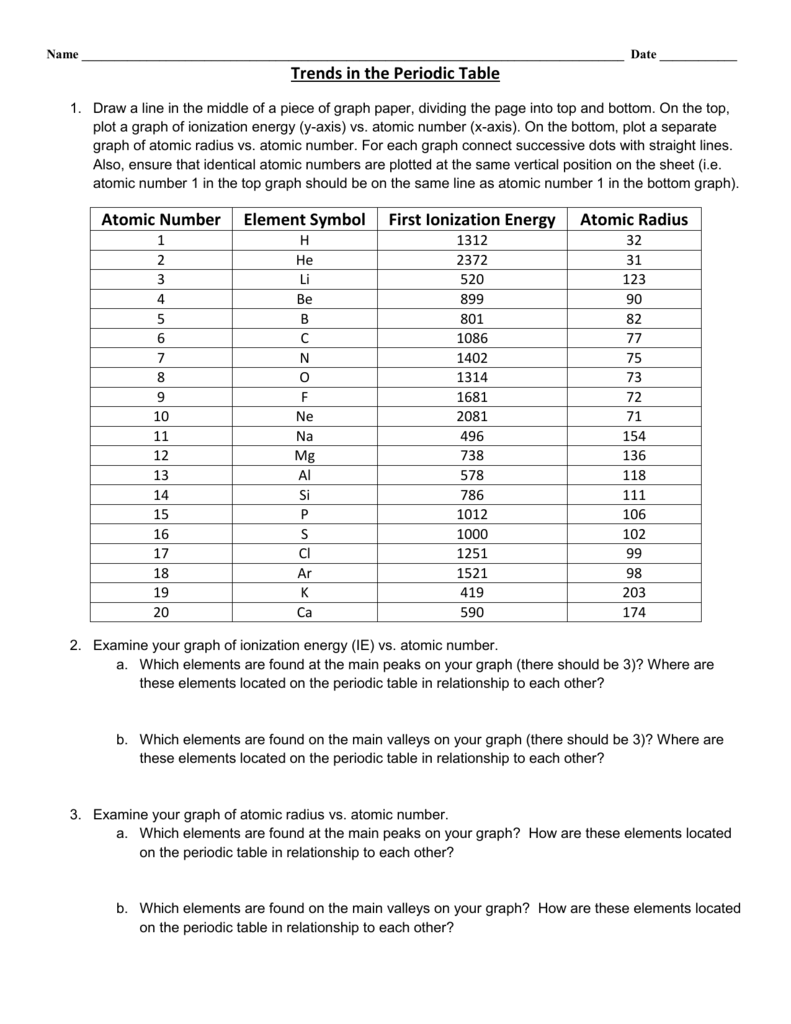
Atomic Radius Trend Periodic Table
Mini video on ion size. One atomic radius trend occurs as you move left to right across the periodic table moving within a period and the other trend occurs when you move from the top of the periodic table down moving within a group.
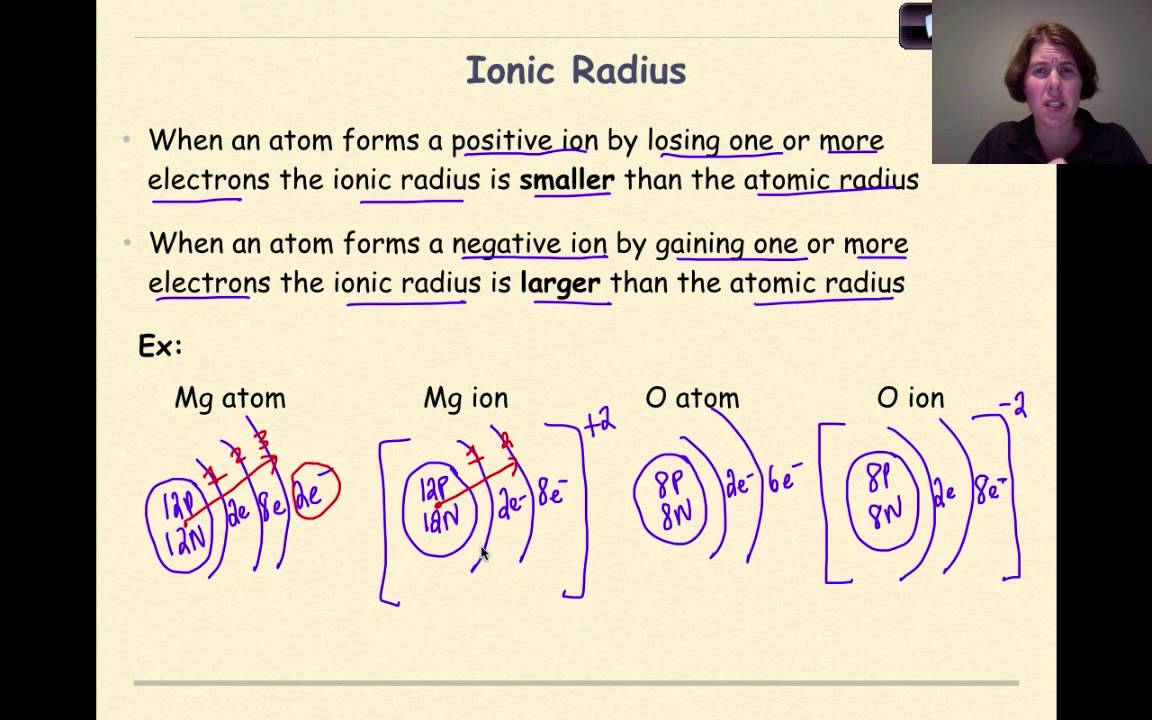
The ionic radius is half the distance between atomic ions in a crystal lattice.
Atomic radius trend periodic table. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. To find the value ions are treated as if they were hard spheres. Periodic table trends electronegativity atomic radius ionization energy bachan thakur october 5 2017 leave a comment in the periodic table elements are categorized based on their electronic structure.
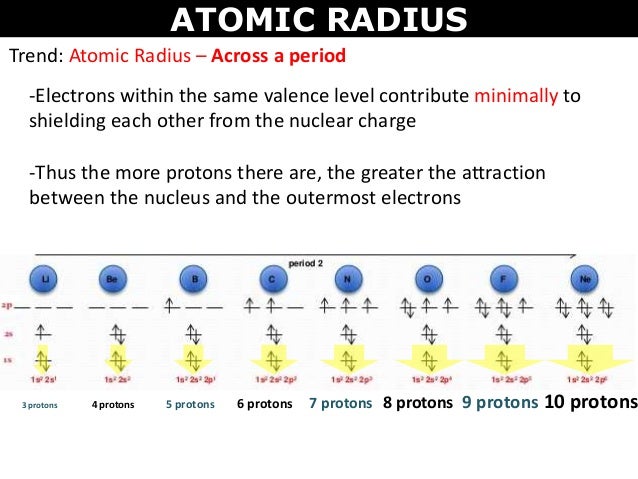
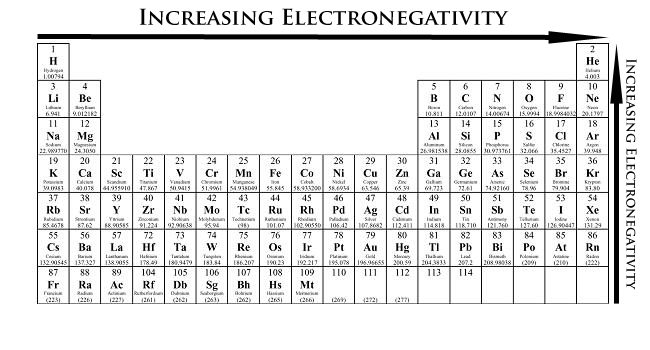
These related values display the same trend in the periodic table. With the above image courtesy of webelements it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Thus the increasing number of nucleus attracts the more electrons more tightly.
Lets think a little bit about the notion of. This is the currently selected item. Atomic and ionic radii.
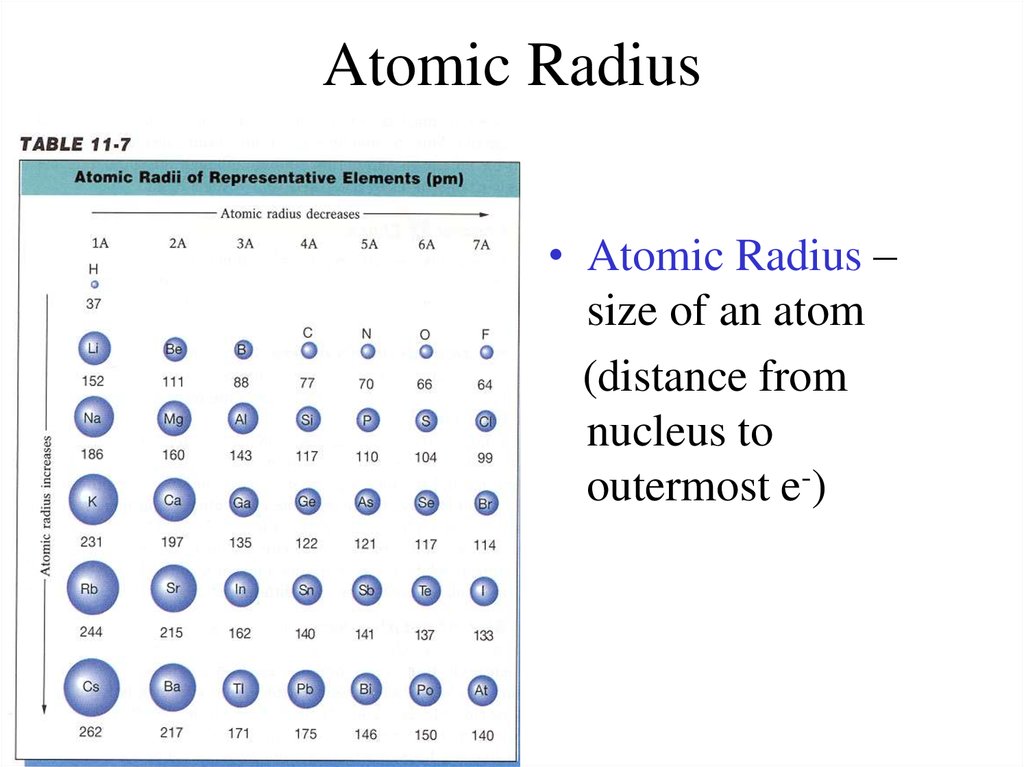
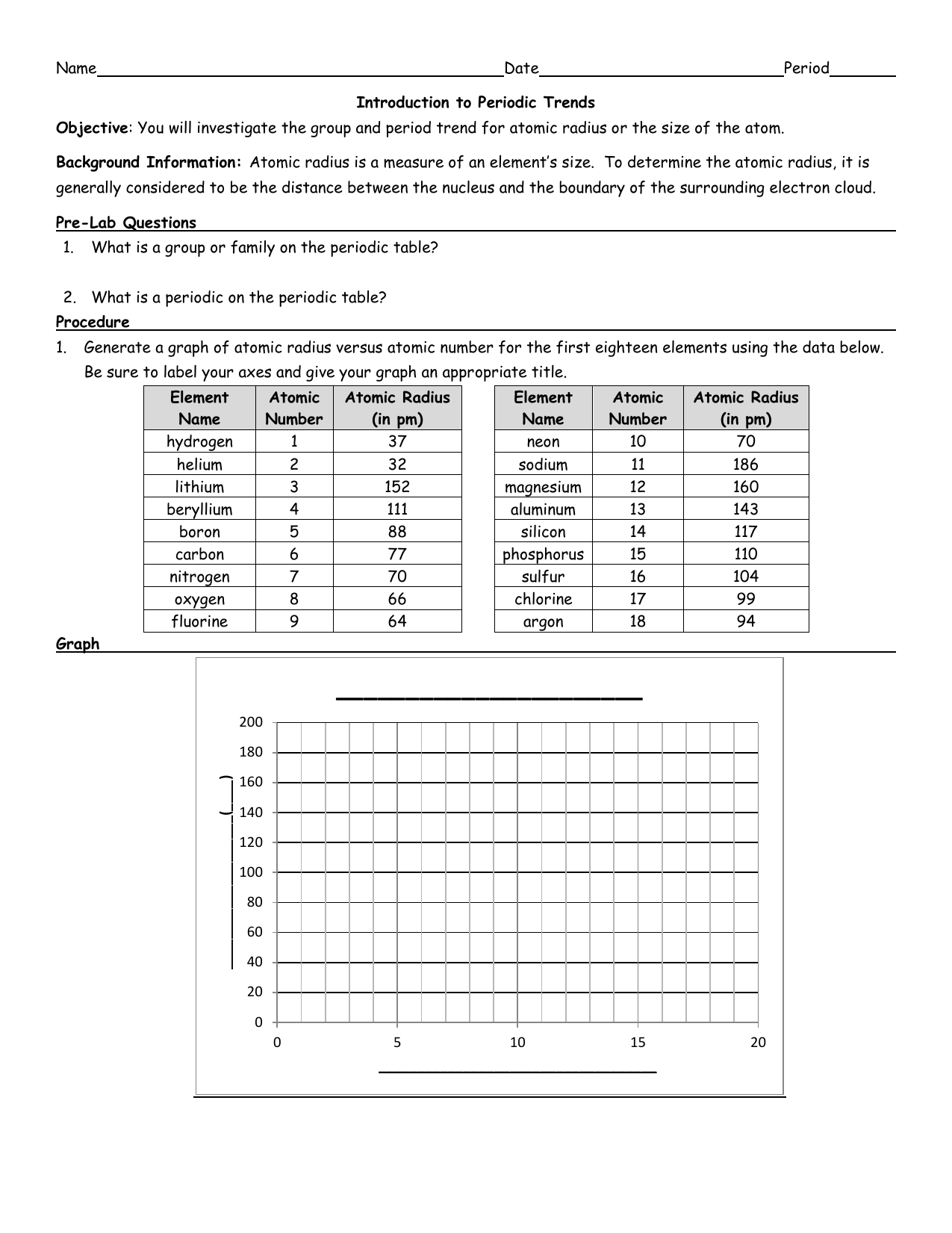
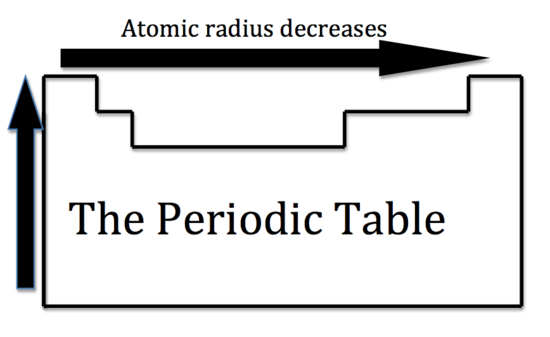
The atomic radius is one half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms just like a radius is half the diameter of a circle. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. Atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost stable electron while ionic radius is half the distance between two atomic nuclei that are just touching each other.
First and second ionization energy. As you move down a column or group the ionic radius increases. This is because each row adds a new electron shell.
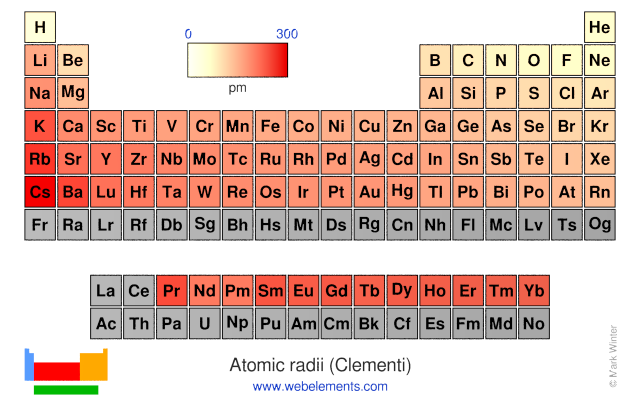
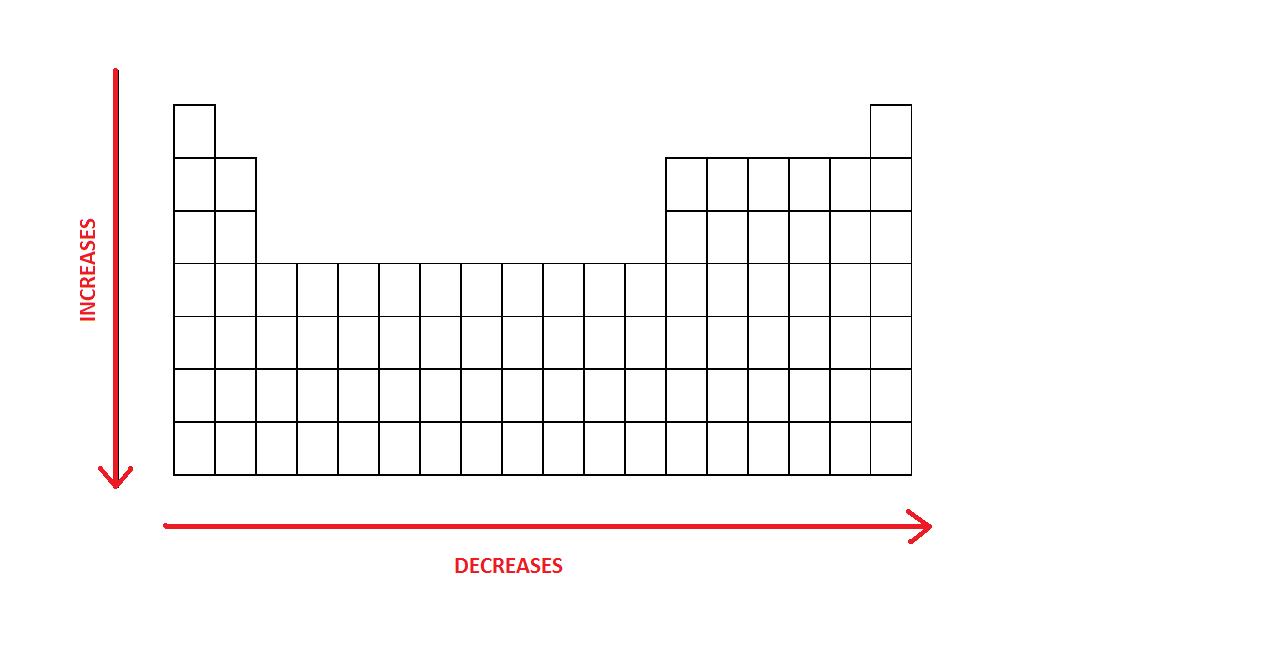
Some are bound by covalent bonds in molecules some are attracted to each other in. The general trend of atomic radius is that it increases as you move down a group and decreases as you move to the right across a period. There are two main atomic radius trends.
Below is a periodic table with arrows showing how atomic radii change to help you. However this idea is complicated by the fact that not all atoms are normally bound together in the same way. While the atomic radius can be defined in a number of different ways the general atomic radius trend across the periodic table holds true.
The atomic radius increases as you move down a column because for every new row of the table a new electron shell is added to the atom. The size of an elements ionic radius follows a predictable trend on the periodic table. Atomic radius in the periodic table.
The atomic radius in the periodic table decreases across the period and increases down the group. Atomic radius trends on periodic table. There are some small exceptions such as the oxygen radius being slightly greater than the nitrogen radius.
The atomic radius for atoms of an element tends to go up as you move down a group of elements in the table. Atomic radius decreases across the period. Within a period protons are added to the nucleus as electrons are being added to the same principal energy level.
Moving from left to right across a period the number of protons and electrons increases while the number of energy shells stay same. These electrons are.












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)










0 Response to "Atomic Radius Trend Periodic Table"
Post a Comment